Zurück 1/1
fme_1043185 - ANIMALS Médaille animalière - Dauphin
80.00 €
Menge
In den Warenkorb

Type : Médaille animalière - Dauphin
Datum: 1978
Name der Münzstätte / Stadt : Monnaie de Paris
Metall : Bronze
Durchmesser : 81 mm
Stempelstellung : 12 h.
Graveur BRET Sylvain (1937-)
Gewicht : 219,30 g.
Rand lisse + corne BRONZE + 1978
Punze : corne BRONZE
Kommentare zum Erhaltungszustand:
Patine hétérogène avec des taches d’oxydation et quelques concrétions. Présence de coups et rayures, notamment sur la tranche
N° im Nachschlagewerk :
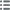
Vorderseite
Titulatur der Vorderseite ANÉPIGRAPHE.
Beschreibung Vorderseite Tête de dauphin sortant de l’eau à droite.
Rückseite
Titulatur der Rückseite ANÉPIGRAPHE.
Beschreibung Rückseite Trois dauphins bondissant hors de l’eau. Signé : S. B.
Kommentare
Dauphin est un nom vernaculaire ambigu désignant en français certains mammifères marins et fluviaux appartenant à l'ordre des Cétacés. Comme les autres cétacés, leur front bombé contient le « melon », une cavité remplie de diverticules du système respiratoire qui communiquent entre eux par des valves. C'est en envoyant de l'air d'un diverticule à l'autre qu'ils émettent des sons. Pour repérer leurs proies, les dauphins utilisent leur sonar. Ils dirigent les sons qu'ils émettent dans la direction de leurs futures victimes, le son ricoche et revient avec un son modifié jusqu'à l'oreille du dauphin. Il se propulse hors de l'eau grâce à sa nageoire caudale..
Dolphin is an ambiguous vernacular name in French designating certain marine and river mammals belonging to the order Cetacea. Like other cetaceans, their domed forehead contains the \\\"melon,\\\" a cavity filled with diverticula of the respiratory system that communicate with each other by valves. It is by sending air from one diverticulum to another that they emit sounds. To locate their prey, dolphins use their sonar. They direct the sounds they emit in the direction of their future victims, the sound ricochets and returns with a modified sound to the dolphin's ear. It propels itself out of the water using its caudal fin.
Dolphin is an ambiguous vernacular name in French designating certain marine and river mammals belonging to the order Cetacea. Like other cetaceans, their domed forehead contains the \\\"melon,\\\" a cavity filled with diverticula of the respiratory system that communicate with each other by valves. It is by sending air from one diverticulum to another that they emit sounds. To locate their prey, dolphins use their sonar. They direct the sounds they emit in the direction of their future victims, the sound ricochets and returns with a modified sound to the dolphin's ear. It propels itself out of the water using its caudal fin.








 Berichten über einen Fehler
Berichten über einen Fehler Die Seite drucken
Die Seite drucken Teilen meiner Auswahl
Teilen meiner Auswahl Stellen Sie eine Frage
Stellen Sie eine Frage Einlieferung/Verkauf
Einlieferung/Verkauf
 Details
Details












