fme_683901 - DRITTE FRANZOSISCHE REPUBLIK Médaille, Union centrale des Arts Décoratifs, Ministère des Finances
120.00 €
Menge
In den Warenkorb

Type : Médaille, Union centrale des Arts Décoratifs, Ministère des Finances
Datum: 1882
Metall : Bronze
Durchmesser : 50,5 mm
Stempelstellung : 12 h.
Gewicht : 59,47 g.
Rand lisse + corne BRONZE
Punze : corne BRONZE
Kommentare zum Erhaltungszustand:
Patine marron hétérogène avec une légère usure sur les reliefs. Présence de quelques coups. La médaille est conservée dans un écrin cartonné bordeaux
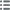
Vorderseite
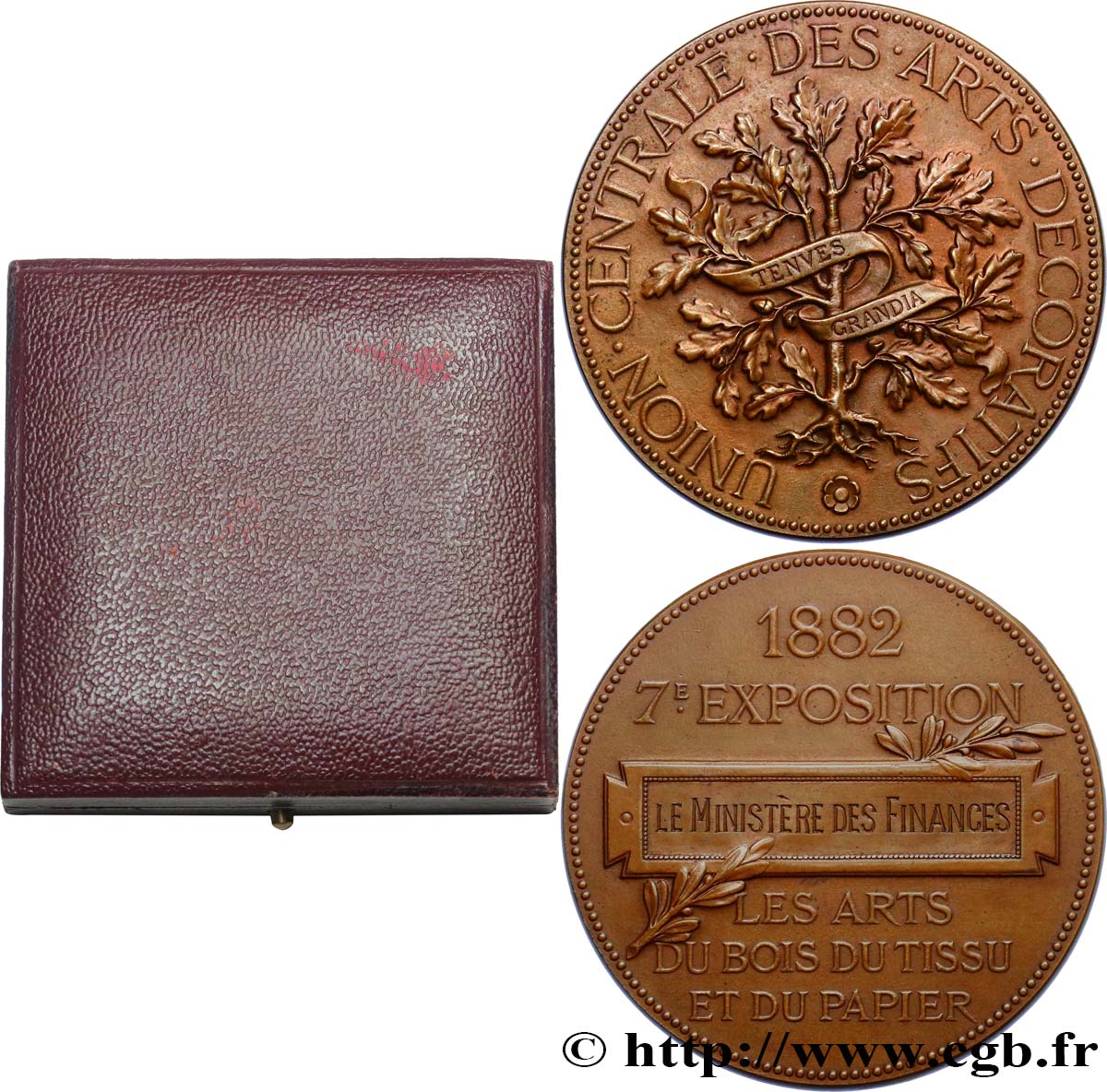
Titulatur der Vorderseite UNION CENTRALE DES ARTS DÉCORATIFS.
Beschreibung Vorderseite Chêne avec les racines nues, portant un ruban inscrit TENVES GRANDIA.
Rückseite
Titulatur der Rückseite 1882 / 7.E EXPOSITION // LE MINISTERE DES FINANCES // LES ARTS / DU BOIS DU TISSU / ET DU PAPIER.
Beschreibung Rückseite Cartouche posé sur une branche de lauriers ; légende en 2 et 3 lignes.
Kommentare
Médaille attribuée au ministère des finances. Ce chène avec le ruban inscrit TENVES GRANDIA est toujours le symbole du Musée des Arts Décoratifs de Paris.
Le musée des arts décoratifs de Paris est un musée parisien qui a pour objectif la valorisation des beaux-arts appliqués et le développement de liens entre industrie et culture, création et production. Il conserve l'une des plus importantes collections d'arts décoratifs au monde. Le musée poursuit l'objectif qui a présidé à sa fondation : « entretenir en France la culture des arts qui poursuivent la réalisation du beau dans l’utile ».
Le musée est situé rue de Rivoli. Il a été inauguré le 29 mai 1905 dans l’aile de Marsan du palais du Louvre à la suite d'aménagements dirigés par l’architecte Gaston Redon.
Il fait partie de l’ensemble plus vaste de l’Union centrale des arts décoratifs (UCAD), une association privée fondée en 1882.
Connue jusqu’en 2005 sous la dénomination d’Union centrale des arts décoratifs (UCAD), elle a été fondée en 1882 par des collectionneurs et des industriels désireux de mettre en valeur les arts appliqués en créant des liens entre industrie et beaux-arts pour « entretenir en France la culture des arts qui poursuivent la réalisation du beau dans l’utile ». Reconnue d’utilité publique quelques mois après sa création, l’association remplit des missions de conservation de collections publiques, de diffusion culturelle, de soutien à la création, d’éducation artistique et de formation de professionnels..
Medal awarded to the Ministry of Finance. This oak tree with the ribbon inscribed TENVES GRANDIA is still the symbol of the Museum of Decorative Arts in Paris.
The Musée des Arts Décoratifs de Paris is a Parisian museum whose objective is to promote fine applied arts and to develop links between industry and culture, creation and production.. It houses one of the most important collections of decorative arts in the world. The museum pursues the objective that led to its foundation: \\\"to maintain in France the culture of the arts which pursue the realization of beauty in utility.\\\".
The museum is located on rue de Rivoli. It was inaugurated on May 29, 1905 in the Marsan wing of the Louvre Palace following renovations directed by the architect Gaston Redon.
It is part of the larger group of the Central Union of Decorative Arts (UCAD), a private association founded in 1882.
Known until 2005 as the Central Union of Decorative Arts (UCAD), it was founded in 1882 by collectors and industrialists wishing to promote applied arts by creating links between industry and fine arts to \\\"maintain in France the culture of the arts which pursue the realization of beauty in utility.\\\". Recognized as being of public utility a few months after its creation, the association fulfills missions of conservation of public collections, cultural diffusion, support for creation, artistic education and training of professionals..
Le musée des arts décoratifs de Paris est un musée parisien qui a pour objectif la valorisation des beaux-arts appliqués et le développement de liens entre industrie et culture, création et production. Il conserve l'une des plus importantes collections d'arts décoratifs au monde. Le musée poursuit l'objectif qui a présidé à sa fondation : « entretenir en France la culture des arts qui poursuivent la réalisation du beau dans l’utile ».
Le musée est situé rue de Rivoli. Il a été inauguré le 29 mai 1905 dans l’aile de Marsan du palais du Louvre à la suite d'aménagements dirigés par l’architecte Gaston Redon.
Il fait partie de l’ensemble plus vaste de l’Union centrale des arts décoratifs (UCAD), une association privée fondée en 1882.
Connue jusqu’en 2005 sous la dénomination d’Union centrale des arts décoratifs (UCAD), elle a été fondée en 1882 par des collectionneurs et des industriels désireux de mettre en valeur les arts appliqués en créant des liens entre industrie et beaux-arts pour « entretenir en France la culture des arts qui poursuivent la réalisation du beau dans l’utile ». Reconnue d’utilité publique quelques mois après sa création, l’association remplit des missions de conservation de collections publiques, de diffusion culturelle, de soutien à la création, d’éducation artistique et de formation de professionnels..
Medal awarded to the Ministry of Finance. This oak tree with the ribbon inscribed TENVES GRANDIA is still the symbol of the Museum of Decorative Arts in Paris.
The Musée des Arts Décoratifs de Paris is a Parisian museum whose objective is to promote fine applied arts and to develop links between industry and culture, creation and production.. It houses one of the most important collections of decorative arts in the world. The museum pursues the objective that led to its foundation: \\\"to maintain in France the culture of the arts which pursue the realization of beauty in utility.\\\".
The museum is located on rue de Rivoli. It was inaugurated on May 29, 1905 in the Marsan wing of the Louvre Palace following renovations directed by the architect Gaston Redon.
It is part of the larger group of the Central Union of Decorative Arts (UCAD), a private association founded in 1882.
Known until 2005 as the Central Union of Decorative Arts (UCAD), it was founded in 1882 by collectors and industrialists wishing to promote applied arts by creating links between industry and fine arts to \\\"maintain in France the culture of the arts which pursue the realization of beauty in utility.\\\". Recognized as being of public utility a few months after its creation, the association fulfills missions of conservation of public collections, cultural diffusion, support for creation, artistic education and training of professionals..








 Berichten über einen Fehler
Berichten über einen Fehler Die Seite drucken
Die Seite drucken Teilen meiner Auswahl
Teilen meiner Auswahl Stellen Sie eine Frage
Stellen Sie eine Frage Einlieferung/Verkauf
Einlieferung/Verkauf
 Details
Details















