Zurück 1/1
fjt_072876 - NORMANDIE (NOBLESSE ET VILLES DE...) Jeton Ar 28, prieur et juges-consuls de Dieppe 1762
Nicht verfügbar.
Artikel auf unserem Online-Shop verkauft (2012)
Preis : 35.00 €
Artikel auf unserem Online-Shop verkauft (2012)
Preis : 35.00 €
Type : Jeton Ar 28, prieur et juges-consuls de Dieppe
Datum: 1762
Metall : Silber
Durchmesser : 28 mm
Stempelstellung : 6 h.
Rand cannelée
Kommentare zum Erhaltungszustand:
Très bel exemplaire avec une usure régulière de circulation
N° im Nachschlagewerk :
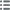
Vorderseite
Titulatur der Vorderseite LUD. XV. REX. - CHRISTIANISS..
Beschreibung Vorderseite Buste lauré et drapé à droite de Louis XV [n° 342] ; au-dessous signature R. FIL. .
Übersetzung der Vorderseite (Louis XV, roi très chrétien).
Rückseite
Titulatur der Rückseite CIVICO. FŒDERE PRODERIT ; À L'EXERGUE EN DEUX LIGNES : ÆDIL. DEPPÆ COMIT./ 1762.
Beschreibung Rückseite Écu aux armes de Dieppe sur un cartouche surmonté d’une tête d’ange et soutenu par deux Néréides ; signature D. V..
Übersetzung der Rückseite (Elle sera utile à l'alliance civile - Assemblée des notables de Dieppe).
Kommentare
Les juridictions consulaires remontent à Henri II. Dans ces lieux de réunions, les marchands élisent entre eux un prieur et deux juges-consuls qui règlent en première instance les problèmes entre négociants. Les juges-consuls ou juges des tribunaux de commerce sont établis par un édit de 1563. Ils étaient souvent d’anciens consuls (officiers municipaux) d’où leur nom. Au XVIIIe siècle, les juges-consuls jugeaient souverainement jusqu’à 500 livres (au-delà, l’affaire relevait des Parlements).
Consular courts date back to Henry II. In these meeting places, merchants elected a prior and two consul judges who settled disputes between traders in the first instance. Consul judges, or judges of the commercial courts, were established by an edict of 1563. They were often former consuls (municipal officers), hence their name. In the 18th century, consul judges had sovereign jurisdiction up to 500 livres (beyond this, the matter fell under the jurisdiction of the Parlements).
Consular courts date back to Henry II. In these meeting places, merchants elected a prior and two consul judges who settled disputes between traders in the first instance. Consul judges, or judges of the commercial courts, were established by an edict of 1563. They were often former consuls (municipal officers), hence their name. In the 18th century, consul judges had sovereign jurisdiction up to 500 livres (beyond this, the matter fell under the jurisdiction of the Parlements).








 Berichten über einen Fehler
Berichten über einen Fehler Die Seite drucken
Die Seite drucken Teilen meiner Auswahl
Teilen meiner Auswahl Stellen Sie eine Frage
Stellen Sie eine Frage Einlieferung/Verkauf
Einlieferung/Verkauf
 Details
Details















