Zurück 1/1
fme_996223 - FUNFTE FRANZOSISCHE REPUBLIK Médaille de la Ville d’Orléans pour Jeanne d’Arc
200.00 €
Menge
In den Warenkorb

Type : Médaille de la Ville d’Orléans pour Jeanne d’Arc
Datum: 1975
Name der Münzstätte / Stadt : 45 - Orléans
Metall : Silber
Der Feingehalt beträgt : 950 ‰
Durchmesser : 67 mm
Stempelstellung : 12 h.
Graveur COUTRE Robert (1915-1970)
Gewicht : 200,30 g.
Rand lisse + 1975 + corne 1ARGENT
Punze : corne 1 ARGENT
Kommentare zum Erhaltungszustand:
Patine hétérogène avec quelques taches d’oxydation. Présence de traces d’usure, coups et rayures
N° im Nachschlagewerk :
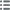
Vorderseite
Titulatur der Vorderseite ORLÉANS.
Beschreibung Vorderseite Vue sur la façade de l'ancien hôtel de ville d'Orléans devenu depuis la mairie d'Orléans appelé aussi Hôtel Groslot. Signé : COUTRE.
Rückseite
Titulatur der Rückseite HOC VERNANT LILIA CORDE.
Beschreibung Rückseite Statue équestre de Jeanne d’Arc, deux blasons au premier plan.
Kommentare
Jeanne d'Arc, née vers 1412 à Domrémy (actuellement dans le département des Vosges en Lorraine), village du duché de Bar dont une partie relevait du royaume de France pour le temporel et de l'évêché de Toul pour le spirituel, et morte sur le bûcher le 30 mai 1431 à Rouen, capitale du duché de Normandie alors possession du royaume d'Angleterre, est une héroïne de l'histoire de France, chef de guerre et sainte de l'Église catholique, surnommée depuis le XVIe siècle « la Pucelle d'Orléans » et, depuis le XIXe siècle, « mère de la nation française ».
Capturée par les Bourguignons à Compiègne en 1430, elle est vendue aux Anglais par Jean de Luxembourg, comte de Ligny, pour la somme de dix mille livres. Elle est condamnée à être brûlée vive en 1431 après un procès en hérésie conduit par Pierre Cauchon, évêque de Beauvais et ancien recteur de l'université de Paris. Entaché de nombreuses irrégularités, ce procès voit sa révision ordonnée par le pape Calixte III en 1455. Un second procès est instruit qui conclut, en 1456, à l'innocence de Jeanne et la réhabilite entièrement. Grâce à ces deux procès dont les minutes ont été conservées, elle est l'une des personnalités les mieux connues du Moyen Âge.
Béatifiée en 1909 puis canonisée en 1920, Jeanne d'Arc est devenue une des quatre saintes patronnes secondaires de la France. Sa fête nationale est instituée par la loi en 1920 et fixée au 2e dimanche de mai.
Joan of Arc, born around 1412 in Domrémy (currently in the Vosges department in Lorraine), a village in the Duchy of Bar, part of which was under the Kingdom of France for temporal matters and the Bishopric of Toul for spiritual matters, and died at the stake on May 30, 1431 in Rouen, capital of the Duchy of Normandy, then a possession of the Kingdom of England, is a heroine of French history, war leader and saint of the Catholic Church, nicknamed since the 16th century \\\"the Maid of Orleans\\\" and, since the 19th century, \\\"mother of the French nation\\\"..
Captured by the Burgundians at Compiègne in 1430, she was sold to the English by Jean de Luxembourg, Count of Ligny, for the sum of ten thousand pounds.. She was condemned to be burned alive in 1431 after a heresy trial led by Pierre Cauchon, Bishop of Beauvais and former Rector of the University of Paris.. Marred by numerous irregularities, this trial was ordered to be revised by Pope Calixtus III in 1455.. A second trial was held which concluded, in 1456, that Joan was innocent and fully rehabilitated her.. Thanks to these two trials, the minutes of which have been preserved, she is one of the best-known figures of the Middle Ages..
Beatified in 1909 and then canonized in 1920, Joan of Arc became one of the four secondary patron saints of France.. Its national holiday was established by law in 1920 and set on the 2nd Sunday in May.
Capturée par les Bourguignons à Compiègne en 1430, elle est vendue aux Anglais par Jean de Luxembourg, comte de Ligny, pour la somme de dix mille livres. Elle est condamnée à être brûlée vive en 1431 après un procès en hérésie conduit par Pierre Cauchon, évêque de Beauvais et ancien recteur de l'université de Paris. Entaché de nombreuses irrégularités, ce procès voit sa révision ordonnée par le pape Calixte III en 1455. Un second procès est instruit qui conclut, en 1456, à l'innocence de Jeanne et la réhabilite entièrement. Grâce à ces deux procès dont les minutes ont été conservées, elle est l'une des personnalités les mieux connues du Moyen Âge.
Béatifiée en 1909 puis canonisée en 1920, Jeanne d'Arc est devenue une des quatre saintes patronnes secondaires de la France. Sa fête nationale est instituée par la loi en 1920 et fixée au 2e dimanche de mai.
Joan of Arc, born around 1412 in Domrémy (currently in the Vosges department in Lorraine), a village in the Duchy of Bar, part of which was under the Kingdom of France for temporal matters and the Bishopric of Toul for spiritual matters, and died at the stake on May 30, 1431 in Rouen, capital of the Duchy of Normandy, then a possession of the Kingdom of England, is a heroine of French history, war leader and saint of the Catholic Church, nicknamed since the 16th century \\\"the Maid of Orleans\\\" and, since the 19th century, \\\"mother of the French nation\\\"..
Captured by the Burgundians at Compiègne in 1430, she was sold to the English by Jean de Luxembourg, Count of Ligny, for the sum of ten thousand pounds.. She was condemned to be burned alive in 1431 after a heresy trial led by Pierre Cauchon, Bishop of Beauvais and former Rector of the University of Paris.. Marred by numerous irregularities, this trial was ordered to be revised by Pope Calixtus III in 1455.. A second trial was held which concluded, in 1456, that Joan was innocent and fully rehabilitated her.. Thanks to these two trials, the minutes of which have been preserved, she is one of the best-known figures of the Middle Ages..
Beatified in 1909 and then canonized in 1920, Joan of Arc became one of the four secondary patron saints of France.. Its national holiday was established by law in 1920 and set on the 2nd Sunday in May.








 Berichten über einen Fehler
Berichten über einen Fehler Die Seite drucken
Die Seite drucken Teilen meiner Auswahl
Teilen meiner Auswahl Stellen Sie eine Frage
Stellen Sie eine Frage Einlieferung/Verkauf
Einlieferung/Verkauf
 Details
Details















