- Accueil
- >
- >
fjt_0686 - BRETAGNE (ÉTATS DE...) CHAMBRE DES COMPTES DE BRETAGNE 1647
Nicht verfügbar.
Artikel auf unserem Online-Shop verkauft (2011)
Preis : 120.00 €
Artikel auf unserem Online-Shop verkauft (2011)
Preis : 120.00 €
Type : CHAMBRE DES COMPTES DE BRETAGNE
Datum: 1647
Metall : Kupfer
Durchmesser : 28 mm
Stempelstellung : 6 h.
Rand lisse
Seltenheitsgrad : R1
N° im Nachschlagewerk :
Vorderseite
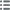
Titulatur der Vorderseite REGIIS RATIONIBVS IVDICANDIS AD ARMOR.
Beschreibung Vorderseite La Justice debout de face, écrasant un dragon.
Übersetzung der Vorderseite Les comptes du Roi doivent être jugés pour le bien de la Bretagne.
Rückseite
Titulatur der Rückseite IVSTIS SPES PACIS IN ARMIS 1647.
Beschreibung Rückseite La Paix ou la France assise à gch. sur des armes,tenant une branche de laurier et une corne d'abondance.
Übersetzung der Rückseite L'espoir de Paix repose sur les armes.
Kommentare
La chambre des comptes de Bretagne est installée à Nantes où elle forme une survivance dans un fief réuni au domaine royal. Comme les autres chambres des comptes du royaume, elle fonctionne avec des comptables qui transmettent leurs comptes au procureur général. Ce dernier les présentaient au Grand bureau de la chambre des comptes où siégeaient des auditeurs et des correcteurs. Enfin, les maîtres jugeaient les comptes en définitif. Dans la réalité, les chambres des comptes provinciales n'étaient d'aucune utilité pour la comptabilité publique et leur rôle consistait à apurer les comptes envoyés par le Conseil du roi sans autre examen.
Ce jeton fait référence aux préliminaires de la Paix de Munster
qui confirme la France dans la possession des Trois-Évêchés de Metz, Toul et Verdun annexés de fait depuis un siècle.
La maison d'Autriche lui cède tous les droits qu'elle possède sur l'Alsace, c'est-à-dire les landgraviats d'Alsace ;
Le Sundgau, comprenant : le comté de Ferrette ; les seigneuries dites médiatisées, à savoir : les seigneuries des Reinach (Montjoie et Hattstatt), des Ribeaupierre (Ribauvillé, Zellenberg, Guémar, Wihr-au-Val, Orbey, la moitié de Sainte-Marie-aux-Mines et Heiteren), de Bollwiller et d'Issenheim ; les terres dites engagées, à savoir : la seigneurie de Hohandsberg, des Schendi ; celle de Hokœnigsbourg et le val de Villé ; la place-forte de Brisach, sur la rive droite du Rhin, et ses dépendances : Hochstetten, Niederrimsingen, Hartheim et Achkarren ainsi que, sur la rive gauche, Biesheim ; Philippsburg ; les droits de bailli sur dix villes de l'empire en Alsace sans Strasbourg ni Mulhouse.
La France annexe la forteresse de Pignerol, dans le Piémont, et Moyenvic, en Lorraine.
De nombreux princes allemands conservent des fiefs en Alsace avant son rattachement à la France. Le traité stipule que leurs possessions ne dépendent pas du droit français mais de celui du Saint Empire romain germanique.
Avec le traité de Münster, la France atteint son but qui est d'agrandir durablement le royaume. L'empereur perd le droit de mener la politique extérieure de l'Empire. Celle-ci est désormais soumis à l'accord du Reichstag. Pour plus de précisions, voir https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trait%C3%A9_de_M%C3%BCnster.
The Brittany Chamber of Accounts is established in Nantes where it forms a survival in a fief united with the royal domain. Like the other audit chambers of the kingdom, it operates with accountants who transmit their accounts to the attorney general.. The latter presented them to the Grand Office of the Chamber of Accounts where auditors and correctors sat.. Finally, the masters judged the accounts definitively. In reality, the provincial audit chambers were of no use for public accounting and their role consisted of clearing the accounts sent by the King's Council without further examination..
This token refers to the preliminaries of the Peace of Munster which confirmed France in possession of the Three Bishoprics of Metz, Toul and Verdun annexed in fact for a century.
The House of Austria cedes to him all the rights it possesses over Alsace, that is to say the landgraviates of Alsace; Sundgau, comprising: the county of Ferrette; the so-called mediatized lordships, namely: the lordships of Reinach (Montjoie and Hattstatt), Ribeaupierre (Ribauvillé, Zellenberg, Guémar, Wihr-au-Val, Orbey, half of Sainte-Marie-aux-Mines and Heiteren), Bollwiller and Issenheim; the so-called engaged lands, namely: the lordship of Hohandsberg, Schendi; that of Hokœnigsbourg and the Val de Villé; the stronghold of Brisach, on the right bank of the Rhine, and its dependencies: Hochstetten, Niederrimsingen, Hartheim and Achkarren as well as, on the left bank, Biesheim; Philippsburg; bailiff's rights over ten cities of the empire in Alsace without Strasbourg or Mulhouse.
France annexes the fortress of Pignerol, in Piedmont, and Moyenvic, in Lorraine.
Many German princes retained fiefs in Alsace before its annexation to France.. The treaty stipulates that their possessions are not subject to French law but to that of the Holy Roman Empire..
With the Treaty of Münster, France achieved its goal of permanently expanding the kingdom.. The Emperor loses the right to conduct the Empire's foreign policy. This is now subject to the approval of the Reichstag.. For more details, see https://fr. Wikipedia. org/wiki/Trait%C3%A9_de_M%C3%BCnster
Ce jeton fait référence aux préliminaires de la Paix de Munster
qui confirme la France dans la possession des Trois-Évêchés de Metz, Toul et Verdun annexés de fait depuis un siècle.
La maison d'Autriche lui cède tous les droits qu'elle possède sur l'Alsace, c'est-à-dire les landgraviats d'Alsace ;
Le Sundgau, comprenant : le comté de Ferrette ; les seigneuries dites médiatisées, à savoir : les seigneuries des Reinach (Montjoie et Hattstatt), des Ribeaupierre (Ribauvillé, Zellenberg, Guémar, Wihr-au-Val, Orbey, la moitié de Sainte-Marie-aux-Mines et Heiteren), de Bollwiller et d'Issenheim ; les terres dites engagées, à savoir : la seigneurie de Hohandsberg, des Schendi ; celle de Hokœnigsbourg et le val de Villé ; la place-forte de Brisach, sur la rive droite du Rhin, et ses dépendances : Hochstetten, Niederrimsingen, Hartheim et Achkarren ainsi que, sur la rive gauche, Biesheim ; Philippsburg ; les droits de bailli sur dix villes de l'empire en Alsace sans Strasbourg ni Mulhouse.
La France annexe la forteresse de Pignerol, dans le Piémont, et Moyenvic, en Lorraine.
De nombreux princes allemands conservent des fiefs en Alsace avant son rattachement à la France. Le traité stipule que leurs possessions ne dépendent pas du droit français mais de celui du Saint Empire romain germanique.
Avec le traité de Münster, la France atteint son but qui est d'agrandir durablement le royaume. L'empereur perd le droit de mener la politique extérieure de l'Empire. Celle-ci est désormais soumis à l'accord du Reichstag. Pour plus de précisions, voir https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trait%C3%A9_de_M%C3%BCnster.
The Brittany Chamber of Accounts is established in Nantes where it forms a survival in a fief united with the royal domain. Like the other audit chambers of the kingdom, it operates with accountants who transmit their accounts to the attorney general.. The latter presented them to the Grand Office of the Chamber of Accounts where auditors and correctors sat.. Finally, the masters judged the accounts definitively. In reality, the provincial audit chambers were of no use for public accounting and their role consisted of clearing the accounts sent by the King's Council without further examination..
This token refers to the preliminaries of the Peace of Munster which confirmed France in possession of the Three Bishoprics of Metz, Toul and Verdun annexed in fact for a century.
The House of Austria cedes to him all the rights it possesses over Alsace, that is to say the landgraviates of Alsace; Sundgau, comprising: the county of Ferrette; the so-called mediatized lordships, namely: the lordships of Reinach (Montjoie and Hattstatt), Ribeaupierre (Ribauvillé, Zellenberg, Guémar, Wihr-au-Val, Orbey, half of Sainte-Marie-aux-Mines and Heiteren), Bollwiller and Issenheim; the so-called engaged lands, namely: the lordship of Hohandsberg, Schendi; that of Hokœnigsbourg and the Val de Villé; the stronghold of Brisach, on the right bank of the Rhine, and its dependencies: Hochstetten, Niederrimsingen, Hartheim and Achkarren as well as, on the left bank, Biesheim; Philippsburg; bailiff's rights over ten cities of the empire in Alsace without Strasbourg or Mulhouse.
France annexes the fortress of Pignerol, in Piedmont, and Moyenvic, in Lorraine.
Many German princes retained fiefs in Alsace before its annexation to France.. The treaty stipulates that their possessions are not subject to French law but to that of the Holy Roman Empire..
With the Treaty of Münster, France achieved its goal of permanently expanding the kingdom.. The Emperor loses the right to conduct the Empire's foreign policy. This is now subject to the approval of the Reichstag.. For more details, see https://fr. Wikipedia. org/wiki/Trait%C3%A9_de_M%C3%BCnster








 Berichten über einen Fehler
Berichten über einen Fehler Die Seite drucken
Die Seite drucken Teilen meiner Auswahl
Teilen meiner Auswahl Stellen Sie eine Frage
Stellen Sie eine Frage Einlieferung/Verkauf
Einlieferung/Verkauf
 Details
Details










